AGENDA - ESD DESIGN & MEASUREMENT: SYSTEMS, SUBSYSTEMS, & EQUIPMENT
In a cold dry environment, like up-north, out in space, or even in Florida where the humidity is 90% outside but only 40% where the equipment is being used, ESD events are possible. Plus, equipment being shipped to Europe and other countries that use the EU EMC requirements must meet ESD limits based upon operational requirements. This presentation covers design and protection of systems and equipment from ESD. An ESD transient doesn't last very long, but it is extreme with a 2-3 Megawatt surge that has high energy to 300 MHz and levels sufficient to cause upset all the way to 1 - 3 GHz. Fortunately some of the most important protection methods are free if they are designed in from the beginning and not added later as a retrofit to a non-functional design.
This presentation covers the five most important design categories for ESD protection: segregation/isolation, PCB/electronics design, cable design, filtering, and shielding.
1. Electron Mobility and Charge Creation
Electron Mobility, Charge Accumulation, and how it occurs
The environment ‘s effect on ESD amplitudes
How ESD couples into systems and destroys semiconductor devices
2. Mechanism of Electro Static Discharge
Triboelectric series
ESD Generated by Floor Materials, Particles, Gases
ESD Damage Levels
Charge Density/Arc Over Distance
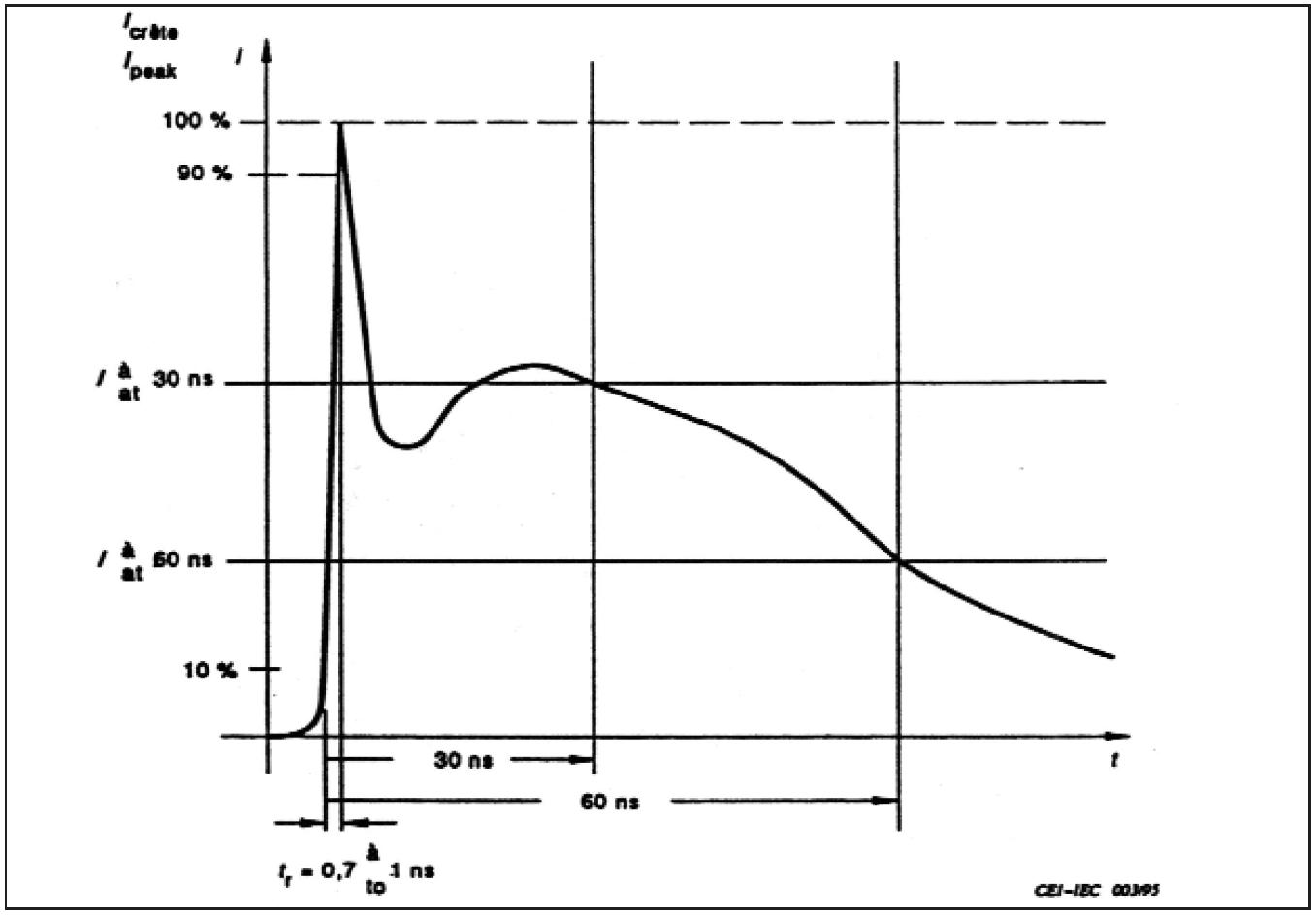
ESD Waveform & Spectrum
Component Failures
3. ESD Coupling into Electronic Systems
ESD Direct and Indirect Discharge Coupling Mechanisms
Radial and Linear ESD Current Flow
Segregation/Isolation
Simplified Loop Pickup Equation
ESD Circuit, I/O & Cable Hardening
4. ESD Circuit, I/O & Cable Hardening
ESD Protection Methods Discussion
ESD protection design of high-speed, logic-based systems
Importance of Multilayer PCB’s
I/O ESD Protection
Differential and Common Mode Radiation Coupling
ESD Control for Interconnect Cables and Connectors
Transient Voltage Suppression Devices
5. Bonding & Grounding
Grounding and Bonding Rationale
Isolating uninsulated grounds
Cable, Connector, Box, and System-Level Grounding
6. Filters & Isolation Transformers
Types of filter designs
Combined Common and Differential–Mode Filter
Filtering Safety Ground
Effect of Parasitic Capacitance and
Poor Mounting on Filter Performance
Typical CM and DM Rejection of Shielded-Isolation Transformers
Combined Shielded-Isolation Transformers and Filters are Not Redundant
7. ESD Shielding
Shielding Effectiveness & Materials
Packaging in Plastic vs Metal
Aperture Attenuation
Aperture Leakage and Its Control
8. ESD Test and Evaluation
Brief Overview IEC 61000-4-2 & IEEE/ANSI ESD Tests
ESD Qualification Test Setup and Testing
Table Top & Floor Standing Equipment
Direct Contact and Air Discharge
Direct Injection Case, Cable, Connector, & Pins
Using ESD as a Diagnostic Procedure
Component ESD Protection
9. Component ESD Protection
Minimum Requirements for an ESD Protected Prototype Construction Area
A significant problem at the workplace
www.ronbrewer